
A Comprehensive Analysis of Aramid Fibers: Properties, Applications, and Future Development
2026-01-28 15:03
Introduction to Aramid
Aramid fiber is a linear polymer composed of aromatic and amide groups. It possesses not only excellent mechanical properties but also a stable chemical structure and ideal mechanical properties.
These characteristics endow aramid fiber with numerous advantages, including ultra-high strength, high modulus, high temperature resistance, acid and alkali resistance, light weight, and wear resistance.
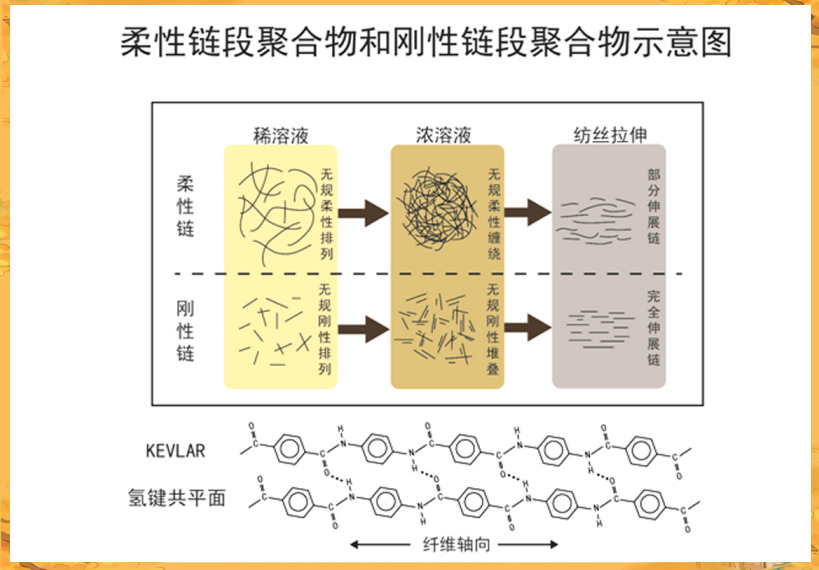
Unlike the molecular chains of ordinary flexible polymers, the main chain structure of aramid fiber is based on the para-position of benzene rings, forming a rod-like molecular structure.
This unique molecular structure makes it difficult for the molecular chain segments to undergo internal rotation, thus exhibiting a linear rigid structure.
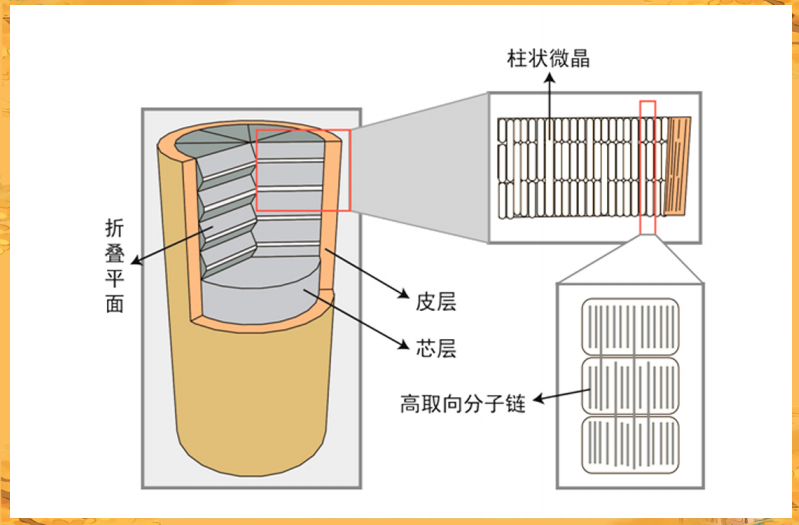
Aramid fibers also exhibit a variety of supramolecular structures, including core-sheath structures, subcrystalline structures, and microfiber structures. The crystallinity of the fiber sheath is lower than that of the core, and the sheath thickness varies depending on the fiber type and spinning process, typically ranging from 0.1 μm to 1 μm.
The core consists of single crystals arranged along the fiber axis, with a slightly lower degree of orientation than the sheath. The molecules in the fiber are almost parallel to the fiber axis in the longitudinal direction, while in the transverse direction they are radially oriented parallel to the hydrogen bond sheets.
On the other hand, meta-aramids, represented by poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMTA) fibers, lack the conjugation effect of covalent bonds in their molecular chains, resulting in lower rotational potential energy within the molecular chains. The macromolecular chains are more flexible than para-aramids, and the fibers also have lower crystallinity.
Applications of aramid fibers
Para-aramid fibers, with their excellent ballistic protection properties, play a key role in the field of military protection,It is also often used as a reinforcement in composite materials, blended with carbon fiber, glass fiber, etc.
Aramid pulp, a highly fibrillated fiber, has a high specific surface area and unique tensile strength and low density properties, making it an ideal reinforcing material in resins, rubbers and other matrices.
The application of meta-aramid fibers means that fabrics made from these fibers play a vital role in industries such as manufacturing, military, firefighting, and motorsports.
Summary and Outlook
Aramid-reinforced pipes have demonstrated significant advantages in the oil and gas pipeline sector, effectively replacing traditional steel pipes and thus preventing leaks caused by corrosion. Furthermore, their lightweight nature simplifies transportation and installation.
The future technological research and development focus of my country's aramid enterprises will be concentrated on the following aspects: improving the performance of aramid through copolymerization modification, optimizing processing and production conditions and reducing fiber costs; and enabling aramid to adapt to different application needs through surface modification, blended fibers and new molding technologies, while improving performance and reducing application costs.






